
In the intricate world of pharmaceutical science, where precision, efficacy, and patient safety are paramount, certain unsung heroes play pivotal roles. Among these, gelatin stands out as a remarkably versatile and enduring biomaterial. Derived from collagen, this natural polymer has, for decades, been a cornerstone in drug formulation and delivery, its applications far exceeding common perception. While many associate gelatin with culinary delights, its sophisticated utility in medicine underscores a legacy of innovation and reliability. This exploration delves into the profound and diverse benefits of pharmaceutical-grade gelatin, illuminating why it remains an indispensable ally in modern healthcare.
The journey of a medicinal compound from laboratory to patient is fraught with challenges. Ensuring stability, palatability, accurate dosing, and optimal absorption requires a carefully selected cast of excipients – inactive substances that serve as vehicles or bulwarks for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Gelatin, with its unique constellation of physicochemical properties, has proven itself to be an exceptionally proficient excipient, contributing significantly to the therapeutic success of countless medications. At Beyond Biopharma, we recognize the critical importance of high-purity, consistently performing materials, and our commitment extends to providing superior pharma-grade gelatin that meets the exacting standards of the industry.
Defining Excellence: What is Pharmaceutical-Grade Gelatin?
Before we navigate its myriad applications, it's crucial to understand what sets pharmaceutical-grade gelatin apart. Unlike its food-grade counterpart, pharma-grade gelatin is manufactured under stringent Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). This ensures exceptionally high levels of purity, minimal endotoxin levels, and a well-defined profile in terms of properties like bloom strength (a measure of gel stiffness), viscosity, particle size, and microbial load. It is meticulously processed to be free from contaminants and to exhibit consistent batch-to-batch performance, a non-negotiable requirement in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Its origin, primarily from bovine or porcine sources, is carefully controlled and traceable to mitigate any risks, such as Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE). For a deeper understanding of the quality and specifications essential for these applications, particularly for capsule manufacturing, resources like Beyond Biopharma's Pharma-Grade Gelatin Particles for Hard Capsules & Soft Gel Products offer valuable insights.
Quick details of Edible Gelatin for Confectionery Application
| Product Name | Edible Grade Bvoine Gelatin |
| Origin of Gelatin | Bovine Skins and Hides |
| CAS Number | 9000-70-8 |
| Color and appearance | Yellow to slightly Yellowish Jelly Pieces |
| Jelly Strength | 80-240 bloom g |
| Moisture | ≤14% |
| Application | Confectionary products like Gummies or Candies |
| Shelf Life | 3 years |
| Packing | 25KGS/ Bag, 500KG/ Pallet. 20MT/ 40' Container |
| Supplying Capacity | 50 MT/month |
Specification of Food Grade Bovine Gelatin
| ITEMS | STANDARD | RESULT | METHODS |
| COLOR | LIGHT YELLOW OR YELLOW | LIGHT YELLOW | --------------------- |
| ODOUR | NORMAL | NORMAL | --------------------- |
| TASTE | NORMAL | NORMAL | ------------------------ |
| TEXTURE | DRIED GRANULES | GRANULES | ------------------------ |
| JELLYSTRENGTH | 180-240BLOOM.G | 200BLOOM | 6.67% AT 10°C FOR 18 HOURS |
| VISCOSITY | 3.5MPa.S ±0.5MPa.S | 3.6Mpa.S | 6.67% AT 60°CAMERICAN PIPETTE |
| MOISTURE | ≤12% | 11.1% | 24 HOURS AT 550°C |
| ASH CONTENT | ≤1% | 1% | COLORIMETRIC |
| TRANSPARENCY | ≥300MM | 400MM | 5% SOLUTION AT 40°C |
| PH VALUE | 4.0-6.5 | 5.5 | SOLUTION 6.67% |
| SO2 | ≤30PPM | 30PPM | DISTILLATION-LODOMETRY |
| HEAVY METAL | ≤30PPM | 30PPM | ATOMIC ABSORPTION |
| ARSENIC | <1PPM | 0.32PPM | ATOMIC ABSORPTION |
| PEROXIDE | ABSENT | ABSENT | ATOMIC ABSORPTION |
| CONDUCTIVITY | PASS | PASS | SOLUTION 6.67% |
| TURBIDITY | PASS | PASS | SOLUTION 6.67% |
| INSOLUBLE | <0.2% | 0.1% | SOLUTION 6.67% |
| TOTAL BACTERIA COUNT | <1000/G | 285/G | EUR.PH |
| E.COLI | Absence in 25 gram | Absent | ABS/25G |
| CLIPBACILLUS | Absence in 25 gram | Absent | EUR.PH |
| SALMONELLA | Absence in 25gram | Absent | EUR.PH |



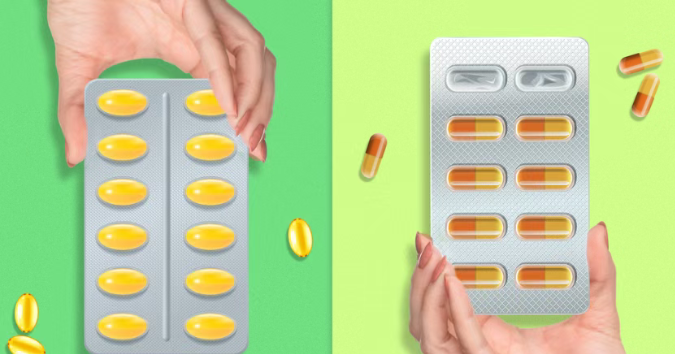
The Bedrock of Oral Dosage: Gelatin in Hard and Soft Capsules
Perhaps the most recognizable pharmaceutical application of gelatin is in the creation of capsules, a preferred dosage form for many patients and manufacturers.
1. Hard Gelatin Capsules: Precision and Protection
Two-piece hard gelatin capsules, often called "hardcaps," are ubiquitous in the pharmaceutical landscape. They consist of a body and a cap, both precisely molded from gelatin solutions. The elegance of this system lies in its simplicity and effectiveness:
● Taste and Odor Masking: Many APIs possess unpleasant tastes or odors. Encasing them within a smooth, tasteless gelatin shell significantly improves patient compliance, especially for chronic medications.
● Precise Dosage Delivery: Hard capsules allow for the accurate filling of powders, granules, pellets, or even semi-solids, ensuring that each dose contains the exact amount of API prescribed.
● API Protection: The gelatin shell provides a robust barrier against environmental factors like light, oxygen, and moisture, which can degrade sensitive APIs, thus preserving drug stability and shelf-life.
● Ease of Swallowing: The smooth surface of gelatin capsules facilitates deglutition, a considerable advantage for patients who have difficulty swallowing tablets.
● Versatility in Formulation: Different types of gelatin (Type A, derived from acid-cured collagen, and Type B, from alkali-cured collagen) offer varying properties. For instance, Type B gelatin often provides greater clarity and film strength, while Type A might be preferred for specific pH compatibility. Bloom strength and viscosity are critical parameters tailored to ensure optimal capsule integrity and dissolution.
2. Soft Gelatin Capsules (Softgels): Enhancing Bioavailability and Appeal
Softgels represent a sophisticated evolution in oral drug delivery. These are one-piece, hermetically sealed gelatin shells containing a liquid or semi-solid fill. Their unique characteristics offer distinct advantages:
● Enhanced Bioavailability: This is arguably the most significant benefit of softgels. They are particularly adept at delivering poorly water-soluble (lipophilic) APIs. By dissolving or suspending the API in an oily vehicle within the capsule, softgels can significantly improve its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. This can lead to lower required doses and a more predictable therapeutic effect.
● Improved Patient Compliance: Like hard capsules, softgels are easy to swallow and effectively mask unpleasant tastes. Their often translucent and colored appearance can also enhance their aesthetic appeal, contributing to better patient acceptance.
● Content Uniformity and Dosage Accuracy: The liquid fill allows for excellent homogeneity of the API, ensuring consistent dosing.
● Tamper-Evidence: The hermetically sealed nature of softgels makes them inherently tamper-evident.
● Protection for Sensitive APIs: The sealed environment offers superior protection against oxidation and hydrolysis for sensitive compounds.
The manufacture of softgels is a marvel of precision engineering, where the gelatin shell is formed, filled, and sealed in a continuous process. Plasticizers like glycerin or sorbitol are incorporated into the gelatin formulation to impart the necessary flexibility and elasticity to the shell.

Expanding Horizons: Gelatin's Diverse Roles Beyond Capsules
While capsules are a prominent showcase, gelatin's utility in pharmaceuticals extends far beyond. Its adaptable nature allows it to perform a spectrum of functions:
● Tablet Manufacturing: The Unseen Contributor
● Binder: In tablet formulations, gelatin can act as a binder, imparting cohesiveness to the powdered ingredients, allowing them to be compressed into a solid, durable tablet.
● Disintegrant: Paradoxically, it can also aid in tablet disintegration. When formulated appropriately, gelatin can absorb gastrointestinal fluids, swell, and help break the tablet apart, releasing the API for absorption.
● Coating Agent: Gelatin solutions can be used to coat tablets, providing a smooth finish for easier swallowing, masking taste, protecting the API, or even enabling controlled-release profiles.
● Wound Healing and Hemostasis: A Biocompatible Scaffold
Gelatin's biocompatibility and biodegradability make it an excellent material for wound care.
● Hemostatic Agent: Absorbable gelatin sponges (e.g., Gelfoam) are widely used in surgical procedures to control bleeding. When applied to a wound, the porous structure of the gelatin sponge absorbs blood and promotes platelet aggregation, facilitating clot formation.
● Wound Dressings: Gelatin-based hydrogels can create a moist wound environment conducive to healing, while also being biodegradable and non-toxic to regenerating tissues. They can absorb exudate and protect the wound bed.
● Vaccine Stabilization: Protecting Life-Saving Immunogens
The stability of vaccines is critical to their efficacy. Gelatin has historically been used as a stabilizer in certain vaccines, particularly live attenuated virus vaccines.
● Lyophilization (Freeze-Drying) Aid: It helps protect the delicate viral or bacterial components during the freeze-drying process and subsequent storage, preventing denaturation and loss of immunogenicity. This is crucial for maintaining the potency of vaccines distributed globally, often under challenging logistical conditions.
● Plasma Expanders: A Historical and Niche Role
In certain situations, particularly in the past or when other options are unavailable, modified fluid gelatins have been used as colloidal plasma expanders. These solutions help to increase or maintain the volume of circulating blood in cases of shock or significant blood loss by exerting oncotic pressure. While newer alternatives are often preferred, gelatin-based expanders have played a vital role and may still find use in specific contexts.
● Emulsifier and Stabilizer in Liquid Formulations:
For liquid dosage forms like suspensions and emulsions, maintaining a uniform distribution of the API is essential. Gelatin can act as an emulsifying and stabilizing agent, preventing the separation of immiscible liquids or the settling of suspended particles, thereby ensuring consistent dosing and product aesthetics.
● Microencapsulation: Precision Delivery Systems
Gelatin is a key material in microencapsulation technologies. This process involves entrapping minute particles or droplets of an API within a gelatin matrix or shell.
● Protection: It shields the API from degradation by environmental factors.
● Controlled Release: The gelatin coating can be designed to release the API at a specific rate or in a targeted location within the body.
● Taste Masking: Effectively conceals the taste of bitter APIs, especially in pediatric formulations.
The Intrinsic Virtues: Why Gelatin Excels
The widespread adoption of gelatin in pharmaceuticals is not accidental; it stems from a unique combination of inherent properties:
● Biocompatibility and Biodegradability: Being a protein derived from natural sources, gelatin is generally well-tolerated by the human body and is broken down by natural enzymatic pathways into amino acids. This minimizes the risk of adverse reactions and ensures it doesn't persist unduly in the system.
● Thermo-reversibility: This is one of gelatin's most celebrated characteristics. It forms a gel when cooled below its setting point and melts back into a liquid (sol) state when heated above its melting point (typically around body temperature). This property is fundamental to the manufacturing of softgels and is also utilized in suppositories and other applications.
● Excellent Film-Forming Capacity: Gelatin readily forms strong, flexible films, which is essential for creating capsule shells and tablet coatings.
● GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) Status: Gelatin has a long and well-documented history of safe use in food and pharmaceutical products, earning it GRAS status from regulatory authorities like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
● Customizable Properties: Manufacturers can select or modify gelatin to achieve specific characteristics. Bloom strength, viscosity, particle size, and isoelectric point can be tailored to suit the demands of a particular formulation or manufacturing process.
Navigating Modern Considerations and Future Innovations
The pharmaceutical landscape is ever-evolving, and gelatin technology continues to adapt:
● Source, Safety, and Purity: Concerns regarding BSE/TSE transmission have led to extremely rigorous sourcing and processing controls for pharmaceutical gelatin. Reputable suppliers ensure that raw materials come from certified BSE-free sources and that manufacturing processes effectively inactivate any potential prions. This unwavering commitment to safety is paramount.
● The Rise of Alternatives and Gelatin's Enduring Strengths: While vegetarian alternatives like Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) and pullulan have gained traction for capsule manufacturing, catering to specific dietary and religious preferences, gelatin often retains advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness, oxygen barrier properties, and its unique thermo-reversibility, which is difficult to replicate. For many applications, gelatin remains the gold standard due to its unparalleled functional profile.
● Advancements in Gelatin Technology: Research continues to unlock new potentials. Modified gelatins, such as succinylated gelatin, offer altered dissolution profiles or reduced cross-linking tendencies. Functionalized gelatins are being explored for sophisticated drug delivery systems, including targeted therapies and regenerative medicine.
The Prudence of Choosing Quality: The Beyond Biopharma Standard
The efficacy, safety, and stability of a pharmaceutical product are inextricably linked to the quality of its constituent excipients. Opting for high-quality, pharma-grade gelatin is not merely a preference but a necessity.
● Consistency and Reliability: Premium gelatin ensures predictable performance in formulations, reducing batch-to-batch variability and manufacturing complications.
● Product Integrity: Superior gelatin contributes to the overall stability and shelf-life of the final drug product.
● Regulatory Compliance: Using well-characterized, high-purity gelatin from a trusted supplier facilitates adherence to stringent global regulatory requirements.
● Patient Safety: Ultimately, the quality of excipients directly impacts patient safety and therapeutic outcomes.
Conclusion: Gelatin – A Timeless Contributor to Health
From the humble capsule to sophisticated drug delivery matrices, gelatin's role in pharmaceutical applications is both profound and pervasive. Its unique blend of biocompatibility, functional versatility, and established safety profile has cemented its position as an invaluable tool in the formulation scientist's arsenal. As pharmaceutical technology advances, seeking more efficient, patient-friendly, and targeted therapies, gelatin, in its refined and evolving forms, is poised to continue its legacy as an indispensable contributor to global health and well-being.
At Beyond Biopharma, we are dedicated to upholding the highest standards in pharma-grade gelatin, empowering innovation and ensuring the quality that patients and manufacturers depend upon. We invite you to explore our offerings and discover how our commitment to excellence can support your pharmaceutical endeavors.
Post time: May-30-2025