Gelatin is one of the most widely used ingredients in pharmaceutical and medical applications, and for good reason: Gelatin is almost universally accepted, has very useful elasticity and transparency, melts at body temperature, and is thermoreversible. Gelatin is a versatile ingredient that offers many advantages in pharmaceutical applications such as capsules and tablets.
Hard and soft gelatin capsules

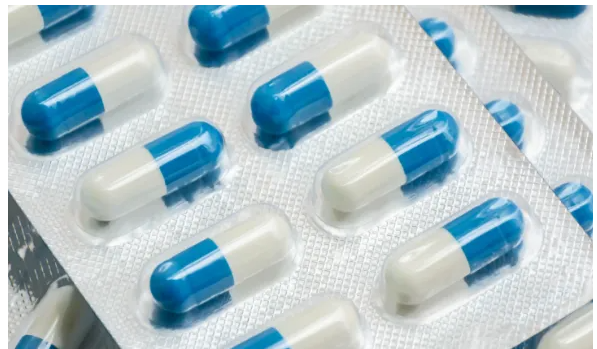

Gelatin is widely used to make the shell of hard and soft capsules, which can effectively protect the contents from light, atmospheric oxygen, pollution and microbial growth, and mask taste and odor.
Hard capsules account for 75% of the gelatin capsule market. Hard capsules, also known as two-piece capsules, consist of two cylindrical capsule shells and a capsule cover that fits tightly to the capsule body to form a sealed whole. Hard capsules range in size from 000 to 5000 capsules (for human use) and can be transparent or colored. Hard capsules can also be stamped. Hard capsules are usually filled with powders, granules, pills and small tablets. They can also be filled with liquids and pastes, using developed sealing and packaging methods while maintaining drug safety standards.

Softgel capsules, on the other hand, feature a one-piece sealed flexible shell that benefits from gelatin’s properties of dissolving in hot water and forming a gel upon cooling. Softgel capsules can be filled with either liquid or semisolid materials and can be made into capsule shells of different shapes and colors.
Although softgel capsules only account for about a quarter of the gelatin capsule market, they offer significant advantages over many traditional oral dosage forms. These advantages include protection of the API, improved swallowability, and ease of dissolution in gastrointestinal fluids. In addition, poorly soluble compounds encapsulated in softgel capsules may be absorbed more efficiently than in traditional dosage forms.
One challenge facing both hard and soft gelatin capsules is cross-linking, which can affect bioavailability. Cross-linking is a natural phenomenon where gelatin molecules become linked to each other and dissolve more slowly due to factors such as humidity, storage temperature, or the chemical nature of the capsule fill. The most well-known compounds that can induce cross-linking reactions in gelatin protein chains are aldehydes, which typically form cross-links with the amino groups of gelatin. Modern solutions can reduce cross-linking in softgel capsules, improving bioavailability by providing better solubility and stability.
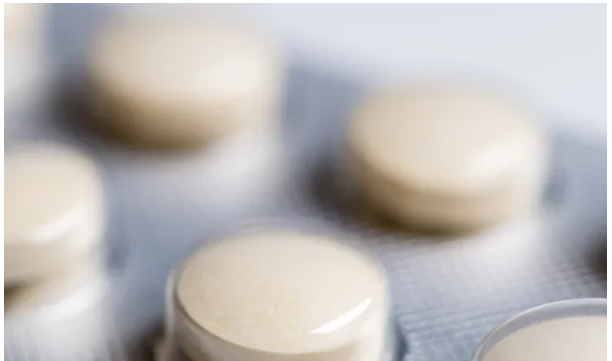
Gelatin can be used as a binder or coating for tablets, providing a lower-cost alternative to capsules. Tablets can also be scored to facilitate dose splitting without the risk of cross-linking.
However, tablets are limited by solid APIs and excipients, have slow dissolution rates, are more difficult to formulate, offer poor protection against oxidation and light, and are more difficult to swallow.
As a binder, gelatin can bind powders such as starch, cellulose derivatives, and gum arabic together during granulation. Gelatin coatings can also help overcome some of the disadvantages of tablets, such as improving swallowability, reducing taste and odor, and helping to protect the API from oxygen and light.
Microencapsulation
The microencapsulation process involves encapsulating particles or droplets in a gelatin shell to form microscopic capsules. Uses include lipophilic vitamins as well as flavors, pigments, pesticides, herbicides, and carbonless copy paper.
Microencapsulation can provide a variety of benefits, including protecting particles from degradation caused by oxygen or light, masking their taste and odor, controlling their release rate, and improving their handling qualities.

Gelatin has several advantages that make it an ideal choice for a range of healthcare applications. It is almost universally tolerated, has excellent cytocompatibility and very low immunogenicity. In addition, it is highly pure, free of contamination risk, and can be produced in a highly reproducible process with easily controlled physical parameters.
Its uses include hemostatic sponges, which not only effectively stop bleeding but are also bioresorbable and promote the migration of new tissue cells, thus accelerating the healing process. Meanwhile, stoma patches use gelatin as a skin adhesive.
Gelatin bone plugs provide stability after joint surgery and do not need to be removed postoperatively due to their biodegradability. Gelatin has a long history of use as a plasma expander and is a relatively cost-effective method of increasing plasma volume. Recently, gelatin has been used in 3D printing to create single-layer structures and multi-layered complex 3D structures for tissue engineering. Its wide range of uses makes gelatin an innovative excipient with decisive advantages.
Post time: Jun-25-2025