collagen, a kind of structural protein in the extracellular matrix, is named Collagen, which evolved from Greek. Collagen is a white, opaque and unbranched fibrous protein mainly found in skin, bone, cartilage, teeth, tendons, ligaments and blood vessels of animals. It is an extremely important structural protein of connective tissues, and plays a role in supporting organs and protecting the body. Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals, accounting for 25% to 30% of the total protein in the body, equivalent to 6% of the body weight.
In recent years, with the development of collagen extraction technology and in-depth studies on its structure and properties, the biological functions of collagen hydrolysates and polypeptides have gradually been widely recognized. The research and application of collagen has become a research hotspot in medical, food, cosmetics and other industries.
In addition to tryptophan and cysteine, collagen contains 18 amino acids, 7 of which are essential for human growth. The glycine in collagen accounts for 30%, and the proline and hydroxyproline together account for about 25%, which is the highest among all kinds of proteins. The content of alanine and glutamic acid is also relatively high. In addition, it also contains hydroxyproline and pyroglutamic acid, which are rarely seen in common proteins, and hydroxyllysine, which is almost absent in other proteins.
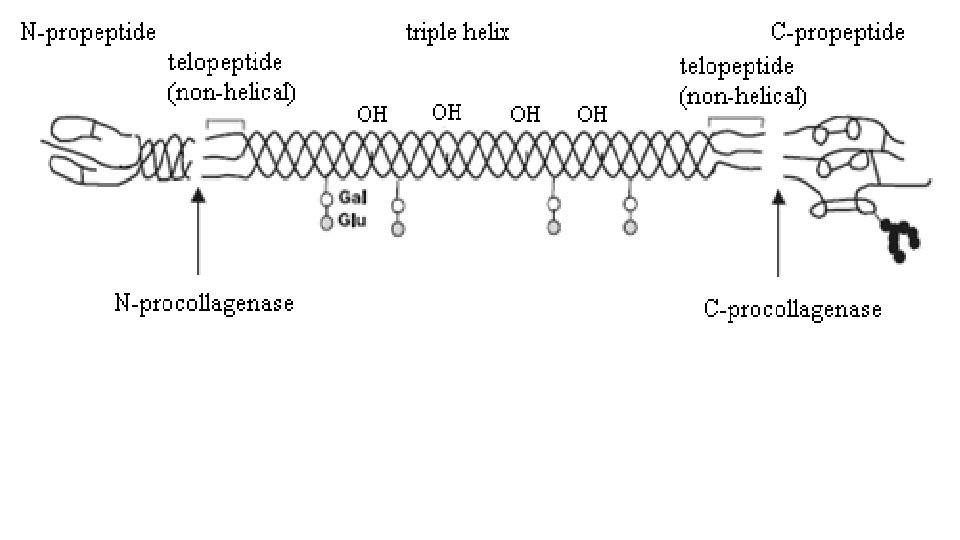
Collagen is a structural protein in the extracellular matrix in which its molecules are aggregated into supramolecular structures. The molecular weight is 300 ku. The most common structural feature of collagen is a triple helix structure, which consists of three alpha polypeptides in a left-handed alpha chain, each of which is twisted around to form a right-handed alpha helix structure.
The unique triple helix structure of collagen makes its molecular structure very stable, and it has low immunogenicity and good biocompatibility. The structure determines the property, and the property determines the use. The diversity and complexity of collagen structure determine its important position in many fields, and collagen products have a good application prospect.
Collagen is a family of proteins. At least 30 coding genes of collagen chains have been found, which can form more than 16 kinds of collagen molecules. According to their distribution and functional characteristics in vivo, collagen is currently divided into interstitial collagen, basal membrane collagen and pericellular collagen. Interstitial collagen molecules account for the vast majority of collagen in the whole body, including type Ⅰ, Ⅱ and Ⅲ collagen molecules, which are mainly distributed in skin, tendon and other tissues, among which type Ⅱ collagen is produced by chondrocytes. Basement membrane collagen is usually referred to as type Ⅳ collagen, which is mainly distributed in the basement membrane. Pericellular collagen, usually type Ⅴ collagen, is present in abundance in connective tissue.
Our Packing is 25KG collagen type put into a PE bag, then the PE bag is put into a fiber drum with a locker. 27 drums are palleted onto one pallet, and one 20 feet container is able to load around 800 drums that is 8000KG if palleted and 10000KGS if not palleted.
Free samples of around 100 grams are available for your testing upon request. Please contact us to request a sample or quotation.
We have professional sales team which provides fast and accurate response to your inquiries. We promise you will receive a response to your inquiry within 24 hours.
Post time: Dec-05-2022